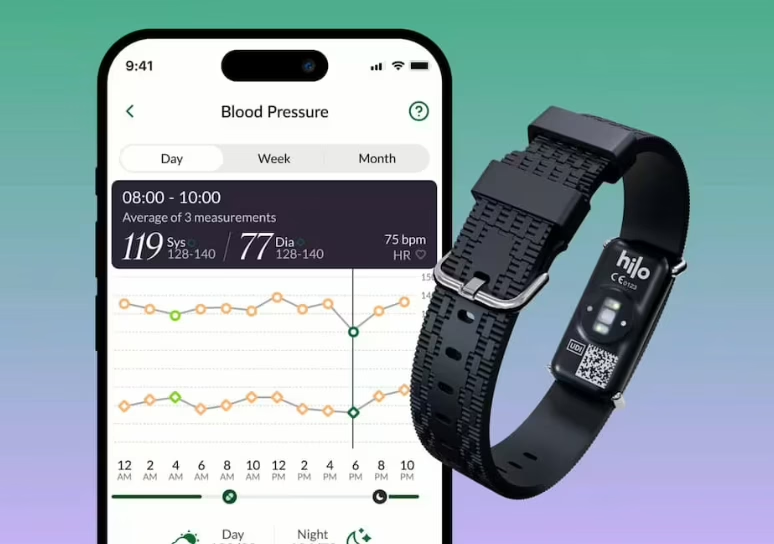
A compact week: small but pointed rounds in diagnostics and patient safety, a urology partnership scaling across EMEA, radiosurgery planning cleared on both sides of the Atlantic, and a headline corporate restructure.
People on the move

Exstent (UK) – Vascular surgeon Matt Thompson becomes CEO to drive commercialization of patient-specific aortic support.
Money flows

Self.co, formerly known as Allergomedica, (Lithuania) a €2.56M mixed grant + venture to scale molecular allergy testing and expand into the UK, Ireland, Austria and Germany; grant component from Innovation Agency Lithuania.

Enteral Access Technologies (UK) a £500K bridging round to scale DoubleCHEK, its CO₂+pH nasogastric tube placement safety device; building UK adoption and early EU rollout.
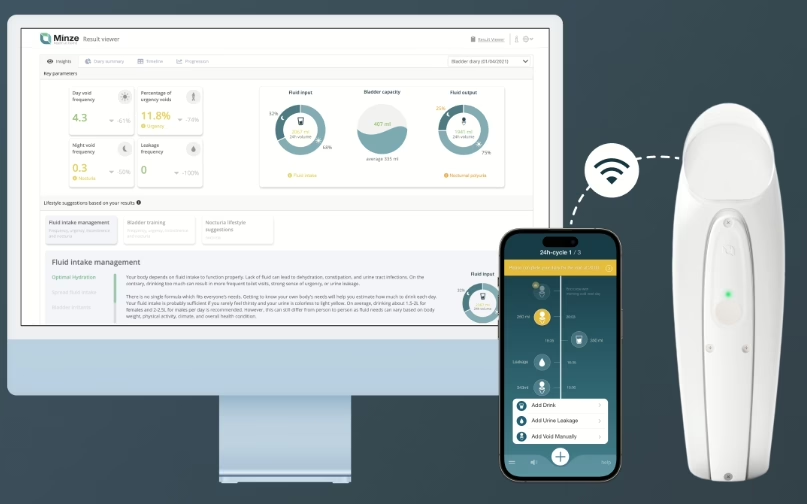
Minze Health (Belgium) × Medtronic: a three-year EMEA partnership to offer Minze’s automated bladder diary (Diary Pod) to patients receiving Medtronic sacral neuromodulation therapy; strengthens digital urology care pathways.
On the press
• ZAP Surgical: ZAP-Axon radiosurgery planning system receives both EU CE certification and US FDA 510(k); enables clinical use across the EU and US.
• Siemens to deconsolidate Healthineers: Siemens plans a direct spin-off of 30% of its ~67% stake to shareholders, cutting to ~37% and targeting <20% medium-term; expect governance/strategic autonomy effects for a core European medtech anchor.
• Tele-robotics milestone: Sentante (Lithuania) reports a first-of-a-kind remote robotic stroke procedure in Scotland guided by specialists located in Florida and Dundee; early signal for cross-border neuro-intervention models.
One thing to remember
Seed-stage cash is trickling into practical, reimbursable workflows (diagnostics, patient safety) while scale comes from channel partnerships and regulatory wins; design for distribution and evidence now so you’re ready when the capital tides turn.