Do you know that FDA already approved 521 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices?
PAPNET. The failure of the pioneering AI/ML-enabled test.
Five hundred apps may not surprise you in January 2023, given the noise around Open AI and its GPTChat. However, the first such device, PAPNET Testing System, was approved over 28 years ago. In 1995, the year of Johnny Mnemonic and Ghost in the Shell movies!
Fig.1 Neural net-based (PAPNET, Neuromedical Systems, Suffern, NY) display of squamous cells (Papanicolaou stain) from a balloon smear showing effects of radiotherapy. Marked cell enlargement and vacuolization of cytoplasm are easily recognized.
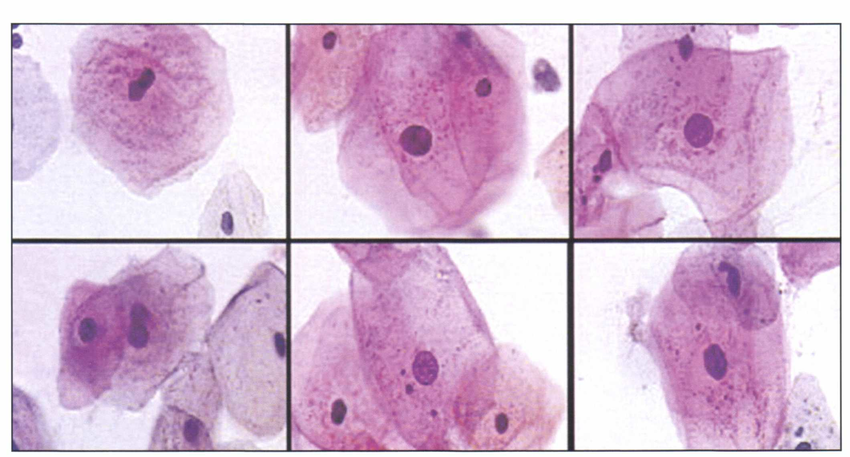
PAPNET was using a neural network to analyze and interpret cytology from Pap smears. While this early system generated a lot of interest and Google Scholar lists 217 peer-reviewed articles on PAPNET results, the business side of it was not that great. The cost-effectiveness of the system in comparison to manual screening by cytotechnician was not there. Neuromedical Systems Inc, the company behind PAPNET went bust in 1999, and now its intellectual property is a part of Becton, Dickinson and Company portfolio.
List of FDA-approved Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices
If you look at the list of approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices, you will notice that the vast majority (392 medical devices, 75% of the whole) are for Radiology. Cardiovascular (57,11%), Hematology (15, 3%), and Neurology (14, 3%) are the remaining three significant categories.
Fig. 2: Split of approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices by Specialty Panel.

There are only 15 companies that have more than five AI/ML-enabled medical devices approved. Five of those companies are actually subsidiaries of GE, which in total owns 42 AI/ML-enabled medical devices. Then there is Siemens with 27 devices, Canon with 15, Aidoc Medical with 13, and Zebra Medical Vision with 9 devices. Philips, which also submitted its devices via different subsidiaries has in total 10 approved AI-enabled devices
Table 1. Companies with over 5 approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices
| Company | AI/ML-enabled medical devices |
|---|---|
| GE Medical Systems | 42 |
| Siemens Healthineers | 27 |
| Canon | 17 |
| Aidoc Medical | 13 |
| Philips Healthcare | 10 |
| Zebra Medical Vision | 9 |
| Quantib BV | 6 |
| Arterys Inc. | 5 |
| Clarius Mobile Health Corp. | 5 |
| HeartFlow, Inc. | 5 |
| RaySearch Laboratories AB | 5 |
| Viz.ai, Inc. | 5 |
The future of AI-enabled and data-driven MedTech
The market for Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning – enabled Medical Devices seems to be poised for growth. At a recent HLTH 2022 conference in Las Vegas, Michelle Wu, CEO of NyquistData, a company offering an AI-supported intelligence platform dedicated to MedTech companies discusses the advantages of using AI to unlock the potential of unstructured data from medical devices.
Source: Xtelligent Healthcare Media
Cleerly. An example of an AI-enabled medical device for a heart-attack-free future.
A good example of upcoming Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning – enabled Medical Device may be Cleerly. The startup has raised $279 million from investors including Fidelity, T. Rowe Price, Novartis and Peter Thiel.
Founded by cardiologist James Min, former professor at Weill Cornell Medical College and director of the Dalio Institute of Cardiovascular Imaging at New York-Presbyterian, Cleerly uses AI to improve diagnostics cutting down on the time it takes to flag patients at risk.
Its proprietary AI algorithms analyze CCTA images to generate a 3D model of patients’ coronary arteries, identify their lumen (the cavity or channel within a tube or tubular organ such as a blood vessel) and vessel walls, locate and quantify stenoses, as well as identify, quantify and categorize plaque.